Spark NLP is a production-ready and fully-featured NLP library that runs natively on Apache Spark. It is already faster on a single machine than other popular NLP libraries let alone in a cluster with multiple machines. In addition, we are constantly optimizing our codes to make them even faster while using fewer resources (memory/CPU). For instance, Spark NLP 4.0 comes with massive optimizations for GPU and modern CPUs for most of our Transformer-based annotators.
That said, some downstream tasks such as Language Models (Transformer models like BERT) or text and token classifiers use Deep Learning via the TensorFlow engine. Therefore, there are ways to optimize them even more by using newer hardware, especially those with accelerations.
The following benchmarks have been done by using a single Dell Server with the following specs:
- GPU: Tesla P100 PCIe 12GB - CUDA Version: 11.3 - Driver Version: 465.19.01
- CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2698 v4 @ 2.20GHz - 40 Cores
- Memory: 80G
GPU
Perhaps the best and the easiest way in Spark NLP to massively improve a DL-based task(s) is to use GPU. Spark NLP comes with a zero-code change feature to run seamlessly on both CPU and GPU by simply enabling GPU via sparknlp.start(gpu=True) or using directly the Maven package that is for GPU spark-nlp-gpu. (more details)
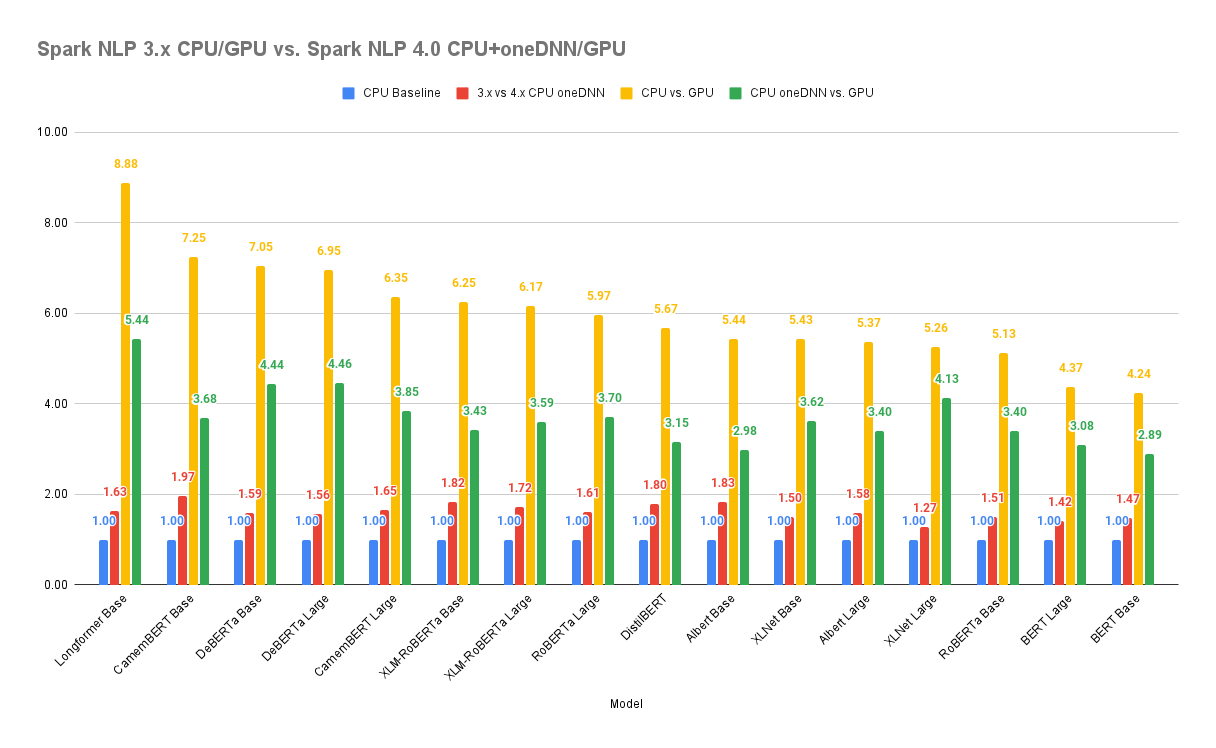
Since the new Transformer models such as BERT for Word and Sentence embeddings are the most computationally available downstream tasks in Spark NLP, we will show a benchmark for inference (prediction) to compare CPU (without any accelerations) to GPU:
.png)
| Model on GPU | Spark NLP 3.4.3 vs. 4.0.0 |
|---|---|
| RoBERTa base | +560%(6.6x) |
| RoBERTa Large | +332%(4.3x) |
| Albert Base | +587%(6.9x) |
| Albert Large | +332%(4.3x) |
| DistilBERT | +659%(7.6x) |
| XLM-RoBERTa Base | +638%(7.4x) |
| XLM-RoBERTa Large | +365%(4.7x) |
| XLNet Base | +449%(5.5x) |
| XLNet Large | +267%(3.7x) |
| DeBERTa Base | +713%(8.1x) |
| DeBERTa Large | +477%(5.8x) |
| Longformer Base | +52%(1.5x) |
Spark NLP 6.1.2 is built with TensorFlow 2.7.1 and the following NVIDIA® software are only required for GPU support:
- NVIDIA® GPU drivers version 450.80.02 or higher
- CUDA® Toolkit 11.2
- cuDNN SDK 8.1.0
CPU
The oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) optimizations are now available in Spark NLP 4.0.0 which uses TensorFlow 2.7.1. You can enable those CPU optimizations by setting the environment variable TF_ENABLE_ONEDNN_OPTS=1.
Intel has been collaborating with Google to optimize its performance on Intel Xeon processor-based platforms using Intel oneAPI Deep Neural Network (oneDNN), an open-source, cross-platform performance library for DL applications. TensorFlow optimizations are enabled via oneDNN to accelerate key performance-intensive operations such as convolution, matrix multiplication, and batch normalization.
This feature is experimental as it has to be enabled manually and benchmarked manually to see whether or not your pipeline can benefit from oneDNN accelerations. That being said, it does not always result in accelerating your annotators as it highly depends on the hardware and the NLP tasks. Similar to GPU, if the task is not computational it won’t change the result and it may even slow down the inferences.
NOTE: Always have a baseline benchmark without having oneDNN enabled so you can compare it with oneDNN. In addition, always make sure you repeat the same steps if you are moving to another hardware (CPU).
Here we compare the last release of Spark NLP 3.4.3 on CPU (normal) with Spark NLP 4.0.0 on CPU with oneDNN enabled. We chose some of the most computational downstream tasks in Spark NLP as they are usually required in the pipeline for other tasks such as NER or text classification):
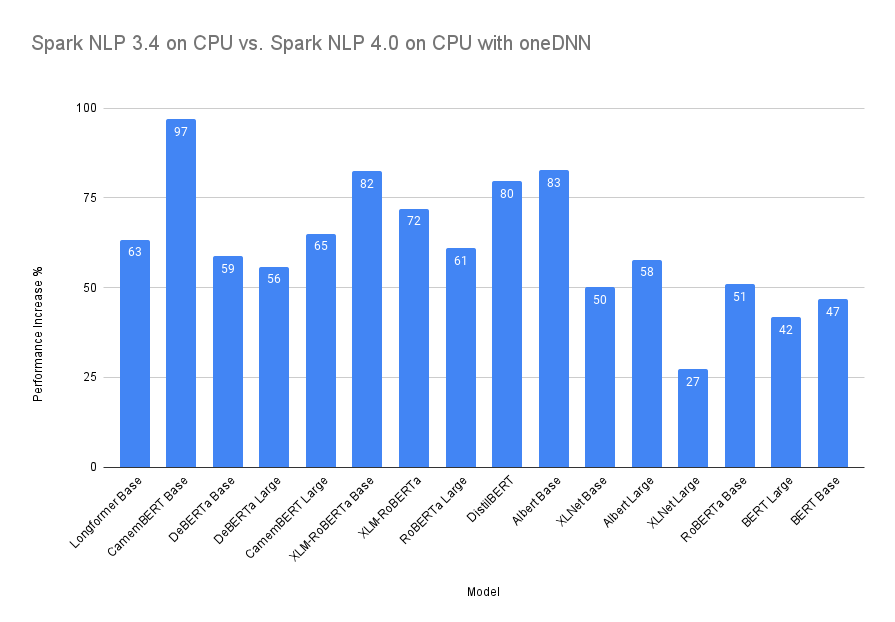
| Model on CPU | 3.4.x vs. 4.0.0 with oneDNN |
|---|---|
| BERT Base | +47% |
| BERT Large | +42% |
| RoBERTa Base | +51% |
| RoBERTa Large | +61% |
| Albert Base | +83% |
| Albert Large | +58% |
| DistilBERT | +80% |
| XLM-RoBERTa Base | +82% |
| XLM-RoBERTa Large | +72% |
| XLNet Base | +50% |
| XLNet Large | +27% |
| DeBERTa Base | +59% |
| DeBERTa Large | +56% |
| CamemBERT Base | +97% |
| CamemBERT Large | +65% |
| Longformer Base | +63% |
In future TensorFlow releases, the oneDNN will be enabled by default (starting TF 2.9) as this feature becomes more stable and more generic for almost all TF ops.
Maximize TensorFlow* Performance on CPU: Considerations and Recommendations for Inference Workloads